Celebrating the 100th anniversary of Wageningen University: Collaboration
This is the fifth blog post in the series about the 100th anniversary of Wageningen University. In this blog post we highlight the collaboration of Wageningen University & Research. Collaboration is visualised using publications indexed in Scopus and data from Staff Publications.
International collaboration
Wageningen University & Research is and always has been a very internationally-oriented university. The share of internationally co-published scientific articles has increased over the past 20 years from 41% to 69% last year. This means that on almost seventy percent of our scientific articles an international co-author is present. Compared to the Dutch and World average this is quite high.
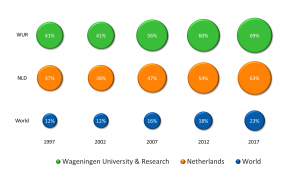
(Source: SciVal, 11-03-2018)
159 countries
Based on Scopus WUR collaborated with 159 different countries since 1918. The word cloud represents the countries by their number of publications together with WUR researchers. The Netherlands is overrepresented in this word cloud, because the WUR affiliation on the article is also counted as a publication from the Netherlands. Generally, researchers collaborate most often with researchers from neighbouring countries; however, many non-European countries are major collaborators for WUR too.

(source: Scopus, 15-2-2018)
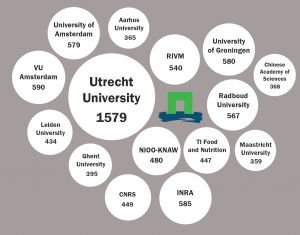
Institutions
The 15 institutions with which WUR collaborates most often (2012-2018) are shown in the picture below, including the number of joint publications (SciVal, 21-4-2018).
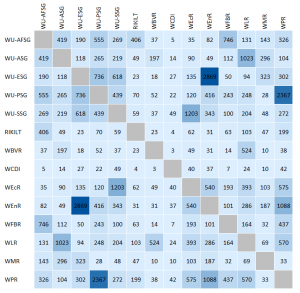
OneWageningen
The synergy between Wageningen University and Wageningen Research is visualised below. The number of joint publications over the past ten years – including both scientific and professional output –between the university departments and the research institutes is shown. Logically, the strongest collaborations are those between the department and the associated research institute. The dark colours indicate the collaborations with the highest joint publications. This is, of course, influenced by the size of the research institutes and university departments.